Abstract
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Moebius sequence comprises a spectrum of brain congenital malformations predominantly affecting the function of multiple cranial nerves. Reported neuroimaging findings are heterogeneous and based on case reports or small case series. Our goal was to describe the neuroimaging findings of Moebius sequence in a large population of patients scanned with MR imaging.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: An observational cross-sectional study was performed to assess brain MR imaging findings in 38 patients with Moebius syndrome studied between 2013 and 2016.
RESULTS: Retrospective analysis of MR imaging studies showed flattening of the floor of the fourth ventricle floor secondary to a bilateral absent facial colliculus in 38 patients (100%) and unilateral absence in 1. A hypoplastic pons was found in 23 patients (60.5%). Mesencephalic malformations consisted of tectal beaking in 15 patients (39.5%) and increased anteroposterior midbrain diameter with a shallow interpeduncular cistern in 12 (31.6%). Infratentorial arachnoid cysts were found in 5 patients (13.2%), and cerebellar vermis hypoplasia, in 2 (5.3%). Supratentorial findings included the following: thalamic fusion (26.3%), periventricular nodular heterotopias (26.3%), ventriculomegaly (26.3%), callosal abnormalities (23.7%), and hippocampal malrotations (23.7%).
CONCLUSIONS: Findings seen in this large patient cohort agreed with previously published reports. Flattening of the fourth ventricle floor secondary to a bilaterally absent facial colliculus was the most frequent MR imaging finding. The presence of other brain stem and cerebellar malformations as well as supratentorial abnormalities may help explain clinical symptoms and achieve a correct diagnosis.
Moebius sequence comprises a spectrum of congenital malformations that mainly affect the function of cranial nerves.1 The estimated incidence of Moebius sequence is 1:250,000 live births with no sex differences.2 This syndrome is clinically characterized by unilateral or bilateral congenital facial paralysis and the failure of ocular abduction with esotropia due to cranial nerve VI palsy.3,4 Because of the predominant involvement of the cranial nerves, Moebius sequence has been classified as forming part of malformations of the midbrain and rhombencephalon.5 Both genetic and nongenetic factors are believed to be important for the development of Moebius sequence.6 Currently, the most accepted etiology of this syndrome is hypoxic-ischemic injury to the brain stem during development, which is supported by histopathologic evaluation of postmortem Moebius sequence brains with evidence of focal necrosis with areas of gliosis and calcification in vascular territories of the brain stem.7
Moebius sequence diagnosis is based on clinical criteria after exclusion of similar syndromes such as congenital fibrosis of the extraocular muscles in which there is severe congenital strabismus, ptosis, and vertical gaze palsy.8,9 MR imaging is helpful to exclude Moebius sequence mimickers and can be useful to confirm the diagnosis. Neuroimaging findings in Moebius sequence have been reported previously. However, reported findings are heterogeneous and based on case reports or small case series.9⇓⇓⇓–13 Consequently, our goal was to describe the neuroimaging findings of Moebius sequence in a large group of patients.
Materials and Methods
Institutional review board (Universidad de Antioquia) approval was obtained for this retrospective study. Between August 2013 and November 2016, a total of 43 patients with the clinical diagnosis of Moebius syndrome were studied with multiplanar noncontrast MR imaging, which included routine imaging sequences. Four patients with partial or complete fusion of the basal ganglia were excluded because a mutation in Tubulin-related genes could not be ruled out. Another patient with neuroimaging features of pontine tegmental cap dysplasia was eliminated from the analysis as well. There were 24 males (63.2%) and 14 females (36.8%) with an average age of 4.1 years (range, 1 month to 25 years). MR imaging studies were independently reviewed by 2 neuroradiologists and 1 neuroradiology fellow. Conflicts among reviewer assessments were resolved by consensus. We analyzed the shape and size of the fourth ventricle, vermis, cerebellum, and cisterns. For the brain stem, we measured the length of the pons and midbrain and assumed that normal was when the former was at least twice the length of the latter. In the supratentorial region, we studied the corpus callosum, gray matter distribution (including the appearance of the basal ganglia), ventricular shape and size, hippocampal shape and size, and subarachnoid spaces.
Means and ranges were calculated for continuous variables. Descriptive statistics with the number of patients and percentages were used for results presentation. All analyses were performed using the software SPSS, Version 26 (IBM, Armonk, New York).
Results
Infratentorial Findings
Flattening of the fourth ventricle floor secondary to an absent bilateral facial colliculus was present in 38 patients (100%). A hypoplastic pons was found in 23 patients (60.5%). Mesencephalic malformations consisted of tectal beaking in 15 patients (39.5%) and increased anteroposterior midbrain diameter with a shallow interpeduncular cistern, in 12 patients (31.6%). Infratentorial arachnoid cysts were found in 5 (13.2%), and cerebellar vermis hypoplasia, in 2 (5.3%).
Supratentorial Findings
Fusion of the thalami was found in 10 patients (26.3%). Periventricular nodular heterotopia was found in 10 subjects (26.3%). Corpus callosum abnormalities were present in 9 patients (23.7%). Hippocampal malrotations were observed in 9 individuals (23.7%). Middle cranial fossa arachnoid cysts were present in 10 patients (26.3%). Ventriculomegaly without imaging criteria for obstructive hydrocephalus was observed in 10 patients (26.3%), and of these, 5 (13.2%) had mostly dilation of the frontal horns. Two patients (5.3%) had hydrocephalus secondary to stenosis of the cerebral aqueduct.
Above-mentioned neuroimaging findings are described in the Table and Figs 1⇓⇓–4.
Neuroimaging findings in 38 patients with Moebius sequence
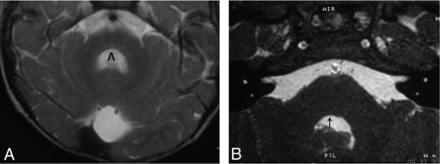
A, Axial T2-weighted image shows bilateral absence of the facial colliculus in the pontine tegmentum with a central depression of the dorsal brain stem. The fourth ventricle has a horseshoe or V shape (inverted V). Pons hypoplasia and a small retrocerebellar cyst are observed. B, A different patient shows absence of only the right facial colliculus (black arrow).
Sagittal T1-weighted image demonstrates a scalloped floor of the fourth ventricle, pontine hypoplasia (pontomesencephalic ratio, <2), tectal beaking with fusion of the inferior colliculi (white arrow), a quadrigeminal arachnoid cyst, and micrognathia. We cannot exclude an abnormal tectum related to mechanical compression by the cyst rather than a malformation by itself.
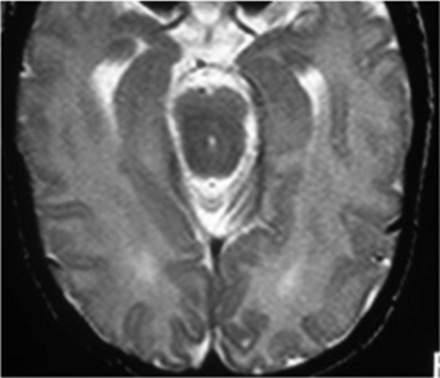
Axial T2-weighted image shows an increase in the anteroposterior diameter of the mesencephalon, fusion of the quadrigeminal inferior colliculi, a very shallow interpeduncular cistern, and ventriculomegaly.
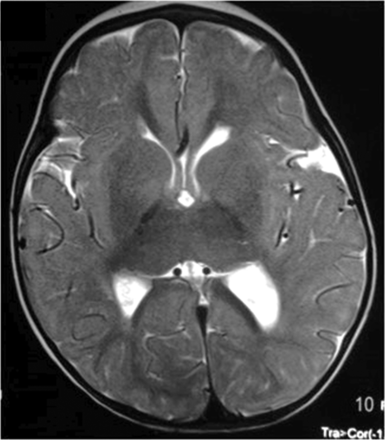
T2-weighted axial image shows thalamic fusion. Small frontal periventricular nodular heterotopias and mild ventriculomegaly are also present.
Discussion
Moebius sequence refers to malformations arising during development of the mesencephalon-rhombencephalon and is classified within the group of early defects of the dorsoventral pattern.5 The term “sequence” is preferred to “syndrome” because it defines a cascade of secondary events after an initial insult during the embryonic period.6 In histopathologic studies of patients affected by Moebius sequence, the main abnormality is found in the pontine tegmentum where the nuclei for cranial nerve VI are located and the intra-axial fibers of the seventh cranial nerve are crossing posterior to these nuclei (the facial colliculus).14
Brain stem ischemia during embryogenesis is the most accepted cause of Moebius sequence. Distribution of branches of the embryonic basilar artery makes the dorsomedial aspect of the brain stem vulnerable to hypoxic-ischemic injury.15 This feature probably explains why hemorrhage and uterine contractions produced by misoprostol have been associated with Moebius sequence.14 Concerning the genetic etiology of Moebius sequence, 2 different loci at 3q21-q22 and 10q have been reported. Additionally, de novo mutations have also been reported affecting the PLXND1 and REV3L genes. These result in a defect in facial branchiomotor neuron migration, supporting these genes as causative for at least a portion of Moebius sequence cases.6 Clinically, patients have unilateral or bilateral congenital facial paralysis and esotropia with preservation of the vertical gaze.
Known brain MR imaging findings in Moebius sequence are based on small case series. The present study includes the largest number of patients reported to date. In our series, the most frequent finding was bilateral absence of the facial colliculus in the pontine tegmentum with flattening of the floor of the fourth ventricle (100%). In axial images, patients showed depression of the floor of the fourth ventricle leading a V or horseshoe shape, a finding that agrees with reports from other authors (Fig 1).10,11,16 One of our patients had unilateral absence of the facial colliculus, and this correlated with the clinical manifestation of unilateral facial paralysis.
The second most frequent finding was pons hypoplasia (60.5%), which, for the purpose of this study, was defined as a pontomesencephalic ratio of <2 (craniocaudal pons length/craniocaudal midbrain length) (Fig 2). Pons and brain stem hypoplasia have been also described by other authors.10,12,13,17 Tectal beaking was present in 39.5% of patients (Fig 2). This finding has only been previously reported in 1 patient and thus is more common than previously believed.12
In almost one-third of our patients, we observed a subjective increase in the anteroposterior diameter of the mesencephalon, similar to that described in the previously mentioned case report (Fig 3).12 We speculate that this finding may be caused by fusion of the inferior mesencephalic tectum colliculus. Its association with a decrease in the amplitude of the interpeduncular cistern remains difficult to explain.
Dysplasia of the corpus callosum and ventriculomegaly were seen with a frequency of 23.7% and 26.3%, respectively. Ventriculomegaly in our study was a less frequent finding than reported by Matsui et al.17 In that publication, 6 of 10 patients showed ventriculomegaly and 3 exhibited prominence of the frontal horns of the lateral ventricles. We found prominence of the frontal horns of the lateral ventricles in 5 (13.2%), and although we did not measure tissue volume, this finding could be explained by white matter volume loss.
Fusion of the thalami was present in 10 patients (26.3%) (Fig 4). This finding was previously described by Pirmez et al16 in an isolated case. These authors found that partial fusion of the thalami was associated with agenesis of the septum pellucidum and frontal horns of the lateral ventricles, concluding that it represented a mild form of lobar holoprosencephaly in association with Moebius sequence. In our study, 1 patient who showed thalamic fusion also had agenesis of the septum pellucidum, but the findings did not fall into the spectrum of holoprosencephaly.
Arachnoid cysts are common in the general population and represent up to 1% of intracranial masses.18 However, in our series, middle cranial fossa and infratentorial arachnoid cysts were observed more frequently in 26.3% and 13.2% of patients with Moebius sequence, respectively. Although the pathogenesis of arachnoid cysts has not been completely elucidated, it has been hypothesized that they could be secondary to an early defect in fetal development coinciding with the appearance of the Moebius sequence.19
Isolated periventricular nodular heterotopia was observed in 26.3% of patients. These malformations of cortical development are the result of arrested neuronal migration. Clinically, patients with these sporadic malformations do not have major intellectual disabilities, and seizures may not appear until the second or third decade of life.20 Our patients with periventricular nodular heterotopia did not have seizures, but because they are young, seizures may occur later in life.
The differential diagnosis of Moebius sequence includes the congenital cranial dysinnervation disorders. In these disorders, MR imaging can show diverse findings such as the absence of the abducens nerve on the affected side in Duane syndrome (related to mutations in CHN1 or SALL4 genes) or extraocular muscle volume loss in congenital fibrosis of the extraocular muscles (mutations in KIF21A, PHOX2A, and TUBB3 genes).21 In our series, we excluded 4 patients with cranial nerve VI and VII palsies because brain MR imaging showed fusion of basal ganglia due to dysgenesis of the anterior arm of the internal capsules, which is a characteristic finding described in the spectrum of tubulinopathies resulting from an abnormal axonal navigation/orientation caused by a mutation in the Tubulin genes.22 Tubulinopathies could not be excluded in those patients because they were not genetically tested; thus, we did not include patients with dysmorphic basal ganglia in this analysis. Last, another condition that should be considered in the differential diagnosis of Moebius sequence is pontine tegmental cap dysplasia (we also excluded another patient with that disorder from the study after analyzing the MR imaging). In this malformation, neuroimaging shows pons hypoplasia associated with tegmental prominence projected into the fourth ventricle (tegmental “cap”) and middle cerebellar peduncle hypoplasia.23 This malformation can be related to deficiencies of multiple cranial nerves and reorganization of white matter tracts.3
Our study has limitations: mainly its retrospective nature, nonquantitative nature, and the absence of a single researcher-defined protocol for imaging acquisition. Nevertheless, because of the relatively large (largest to date) number of patients, we believe our series is unique and important to report.
Conclusions
Findings seen in this large patient cohort agreed with previously published reports. Flattening of the fourth ventricle floor secondary to a bilaterally absent facial colliculus was the most frequent MR imaging finding. The presence of other brain stem and cerebellar malformations as well as supratentorial abnormalities may help explain clinical symptoms and achieve a correct diagnosis.
REFERENCES
- Received December 7, 2018.
- Accepted after revision March 12, 2019.
- © 2019 by American Journal of Neuroradiology